Besides your preference for particular colors, there are coverage and durability considerations in selecting a can of paint color. The main components in a can of paint are resin, pigments, solvents, and additives. Resin is the glue that holds the paint together and allows it to adhere to surfaces (walls, floors, trim, ceilings, etc.). Pigments are solid particles that provide color and coverage. Solvents thin the paint into a liquid form for application to a surface. Additives give additional characteristics to the paint, such as rust or mildew resistance. These four components are part of every untinted can of paint. For ready-made paints or at the point of sale, colorants are liquid paint products that are added to the base to produce the final paint color.
The formulation of paint has a significant effect on the coverage capability of a paint product. The main ingredient that helps paint to have good coverage is titanium dioxide (TiO2). Titanium dioxide is a natural resource mined out of the ground and is also used in other products like toothpaste and deodorant. Titanium dioxide is the most effective and expensive primary white pigment used by paint manufacturers to achieve good coverage. Different paint companies and brands of paint will have a variety of base mix formulas, but the quantity of titanium dioxide will directly affect the coverage ability of the paint.
Before adding colorants, paint bases with a high amount of titanium dioxide will appear pure white. If the paint base appears to have a grey or yellow tone to a white base without any added colorants, there are other pigments in the paint besides titanium dioxide that could result in a final paint product with a slightly muddy color. Besides untinted paint bases, most, if not all, manufacturers have ready-made colors on the shelf that already have colorants or tints in the paint.
The difference in paint mixtures from one company to the next is one of the reasons for the difficulty in matching paint colors from one paint manufacturer to another paint manufacturer. Sometimes, it might not be possible to have an exact match. This is especially true if each manufacturer is using a totally different base color for each mixture. However, paint manufacturers may have a list of colors from other popular paint manufacturers that give an equivalent color match to their own colors. Other manufacturers may use color reader tools to help determine the closest color match. Manufacturers or retailers can also provide color formula labels and crossover lists based on technical data sheets for customers. When viewing this information, locate and compare relevant characteristics to include volume solids, amount of VOCs (volatile organic compounds), film thickness, dry time, etc.
Some popular paint manufacturers are Benjamin Moore, Sherman Williams, Behr, and Valspar. Because of differences in undertones from one manufacturer to the next, architects and designers specifying a color should make sure to include not only the color, but the manufacturer and product as well. Otherwise, the resulting color may have unexpected undertones that conflict with the color of other items or the type of lighting. Paint manufacturers also have specific products developed for applications like residential, commercial, healthcare, industrial, interior, exterior, etc.
Matching one paint to another may be difficult, but matching a paint color to other materials introduces more complexity due to the differences in color properties of each substance. Some of these differences in color may exist between light seen by the eyes and dyes of materials. Paint covers walls and other materials and reflects light, while some materials have color embedded throughout the material. Light is additive based on a green, red, and blue primary color system that combines into white. Physical colors like prints and dyes are subtractive based on a yellow, magenta, and cyan primary color system that combines into black.
Another consideration for paint coverage is that deeper colors tend to have less coverage than lighter colors. This characteristic is directly related to the larger amount of titanium dioxide in lighter paints. Deeper colors tend to have less titanium dioxide, leading to less coverage. In addition, light colors like pastels may only require four to six fluid ounces or less of colorants, while deeper colors like navy blue may necessitate 10 to 14 fluid ounces of colorants. More colorants result in less titanium dioxide base material and less coverage.
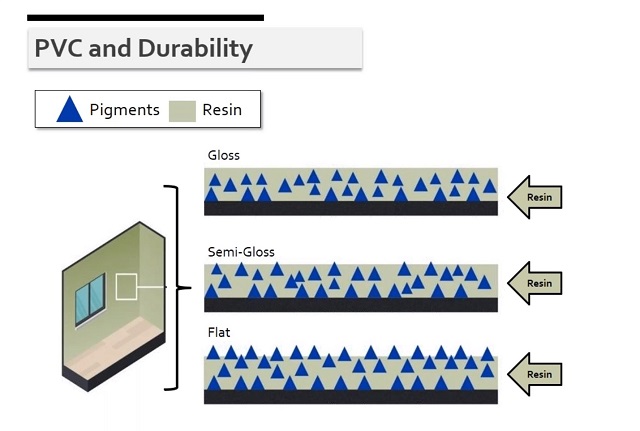
Most people are familiar with the common gloss, semi-gloss, and flat options in paint products. Pigment volume concentration (PVC) of paint affects sheen, durability, and coverage. High gloss paints have less pigments that are completely embedded within the resin, giving less coverage and being harder to cover in repainting the surface. However, the pigment is protected by the resin and this makes the paint more durable and effective for surfaces like doors and trim. Gloss paint finishes can be washed and scrubbed without damaging the paint film. On the other hand, flat paints hold more pigments in the paint that protrudes outside the resin. These protruding pigment particles absorb the light. The pigments are exposed, resulting in a paint with relatively less durability. However, flat paint finishes offer better coverage and can't be washed or scrubbed, but is easier to repaint because of the large amount of pigments. Because of these widely varying characteristics, semi-gloss is a popular option that provides some of the benefits of both gloss and flat gloss paints for many types of paint jobs. Deciding between the finish characteristics of gloss, semi-gloss, and flat finishes involve tradeoffs between sheen, durability, and coverage.
Some environmental conditions that may cause damage and is avoided by good paint durability include abrasion, color rub-off, chalking, cracking, fading, marking, peeling, scrubbing, scuffing, staining, washing, weathering, and UV exposure. One of these conditions, color fading, occurs because of the deterioration of the resin protecting the paint pigments caused by UV exposure. Paints with fade resistance will resist color fade, even with light exposure. Nonetheless, some manufacturers still limit the availability of certain colors for exteriors because testing has revealed unacceptable levels of fade resistance.
Paints with low quality colorants tend to result in a weaker paint film with less durability that can lead to color rub-off. These paints may have less coverage and require additional coats of paint to achieve a particular color with increased drying time for each coat. For example, a deep color with low quality colorants could take three to four days to dry. Higher quality colorants with a resin base, zero VOCs, and no glycols (chemical additives that thins the paint) can actually strengthen and enhance the durability of the paint film.
The best paint product for a particular application will depend on the sheen, durability, and coverage abilities of that product, as well as your preference for a given color. Red and yellow pigments tend not to have high opacity, resulting in less coverage. Blue pigments tend to have relatively more coverage. For maximum durability, a paint with more titanium dioxide is better. This would tend to be a lighter color in a gloss finish. Higher gloss paints provide less coverage, but protect pigments and avoids color rub-off or chalking. Because of the exposed pigments, flat and matte paints tend to have more of these issues, but allow for better coverage. Nevertheless, if you have a preference for a deeper color in either a gloss or flat finish for a specific project, selecting a quality paint product assures that you will still have a good level of coverage and durability.

